Let Futai take you to learn about the “Sheet Metal Laser Cutting” service. This guide can help you better understand and master the technical points of sheet metal laser cutting, so that you can efficiently and accurately complete the cutting task of sheet metal parts without increasing costs.

What is Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a process in which the horizontal laser beam emitted by the laser is transformed into a vertical downward laser beam through a 45° full reflection mirror, and then focused by a lens to form a very small light spot at the focal point. When the light spot is irradiated on the material, the material is quickly heated to the vaporization temperature and evaporated to form holes.
As the beam moves on the material, and with the auxiliary gas (carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, etc.) to blow away the molten waste, the holes are continuously formed into a very narrow (such as about 0.1mm) slit to complete the cutting of the material. Thus, the desired shape or size can be accurately cut. This technology has the characteristics of high precision, high efficiency and high flexibility, and is very suitable for manufacturing laser cutting parts of various complex shapes.
Laser cutting technology plays a key role in industrial development and has become a powerful tool to solve the problems of traditional processing methods.
Metal plate laser cutting process
Sheet metal laser cutting involves the thermal process of using a laser beam to cut fragments from a metal sheet. There are six main cutting methods, such as flame cutting, melting cutting, compressed air cutting, plasma-assisted cutting, gasification cutting and ultra-short pulse laser cutting.
Laser flame cutting: It is the most traditional cutting method. For low-carbon steel materials, oxygen and acetylene or natural gas are used for high-temperature combustion. The chemical reaction releases a large amount of energy (up to five times the laser energy) to assist the laser beam in cutting the material. The advantage is that it is low cost and suitable for thick plates, but the precision is low and it is not suitable for small hole cutting.
Laser Melting cutting: A standard metal cutting process that can also be used to cut other fusible materials, such as ceramics. Use nitrogen or argon to blow away the molten metal and protect the cutting edge from oxidation.
Compressed air cutting: Air pressurized to 5-6 bar is enough to blow away the molten metal in the cut. Since nearly 80% of the air is nitrogen, it is close to melting cutting and is suitable for thin plates.
Plasma-assisted cutting: Plasma-assisted cutting: Select the right parameters to form a plasma cloud composed of ionized metal vapor and cutting gas, accelerate the CO2 laser energy conversion, increase the melting speed, and achieve high-speed cutting.
Gasification cutting: Evaporate the material to minimize the thermal effect on the surrounding material. Use continuous CO2 laser processing to evaporate low-heat, high-temperature The above effect can be achieved by materials that absorb laser light, such as thin plastic films and non-melting materials such as wood, paper, and foam.
Ultrashort pulse laser cutting: After the free electrons in the metal absorb the laser, the temperature rises sharply, the material sublimates directly, and there is no heat conduction to the surrounding area, achieving precise cutting without melting and burrs.
Sheet metal laser cutting processing manufacturer production process video
In-depth understanding of the precision and efficiency of our laser cutting processing. We prove our expertise and strength with our heart.
Advantages of sheet metal laser cutting technology
The advantages of using laser cutting technology are very significant and benefit all kinds of manufacturing environments.
- Good cutting quality: delicate and smooth cutting surface, suitable for high-precision industries.
- High processing efficiency: quickly complete multi-part cutting and improve production efficiency.
- Adjustable incision: flexible control of width and depth to meet diverse needs.
- Wide applicability: applicable to a variety of metal materials and non-metallic materials.
- Precision manufacturing: high precision and high repeatability, achieving micron-level precision.
- Flexible cutting: adapt to different shapes and sizes, and realize complex pattern cutting parts.
- Special-shaped processing: no need for complex molds, reducing production costs.
- One-time forming: reduce subsequent processing, improve processing efficiency, thereby reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
A few disadvantages of metal plate laser cutting
Although metal plate laser cutting has many advantages, it also has defects: high energy consumption, limited cutting of thick metals, and easy formation of hot zones, which cause material melting and deformation, increase damage risk and processing costs. In addition, possible technical challenges include cutting deformation, roughness, verticality and other problems, which affect processing quality and increase costs. Therefore, comprehensive consideration is required in practical applications.
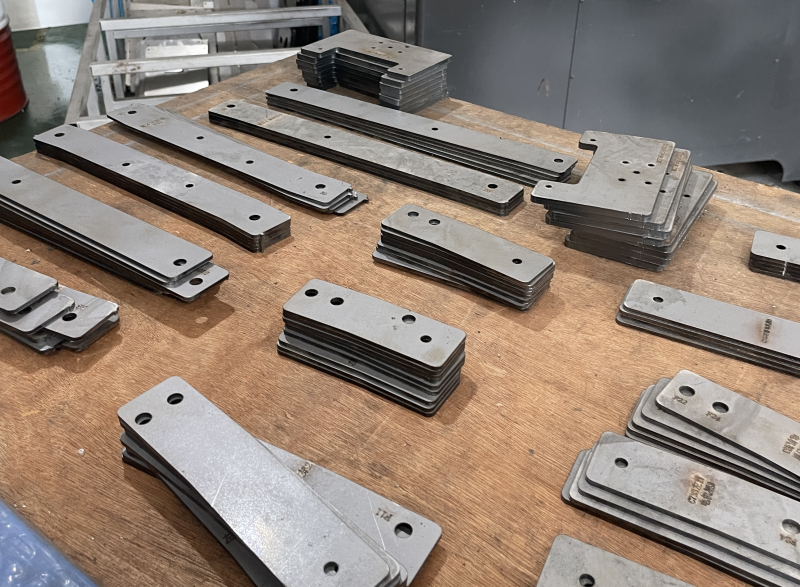

Laser cutting technology applications
Laser cutting technology is widely used to manufacture a wide variety of parts, each of which benefits from the precision and versatility provided by the method.
Structural components: In the mechanical and construction industries, it is used to manufacture structural components such as beams, frames and supports, providing high-precision cutting.
Decorative elements: Produce fine and precise decorative items such as metal panels and artworks, which are widely used in interior design and architecture.
Functional components: In the automotive and mechanical industries, it produces functional components such as gears, brackets and housings to ensure the smooth operation of mechanical systems.
Prototyping: Designers and engineers use it to quickly make prototypes, iterate and improve, and accelerate Product Development.
Electronic Components: The electronics industry produces complex components such as circuit boards and insulation layers, allowing for precise cutting and protection of sensitive materials.
Futai Manufacturers Laser Cutting Services are used in a variety of industries, including: automotive, energy, aerospace, electronics, construction and medical can all benefit from our sheet metal manufacturing.
If your project requires custom sheet metal laser cut parts, or you would like to discuss more related projects together, please contact us today.
What metal materials are suitable for laser cutting?
Metal laser cutting can minimize part deformation and failure. Lasers can cut a variety of materials, such as:
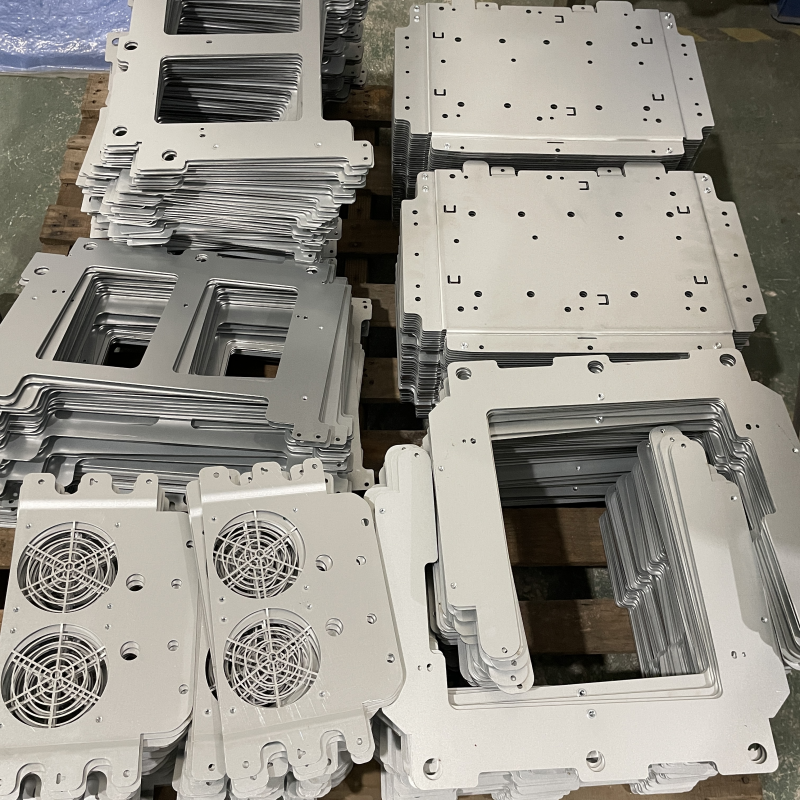

Mild steel/cold rolled steel, also known as carbon steel, steel, cold rolled steel, hot rolled steel.
Sheet metal laser cutting excels at cutting mild steel, where it excels due to its combination of high power and precision. Laser cutters produce a concentrated beam that quickly melts and cuts mild steel, a material that combines strength and ductility. In addition, laser cutting’s versatility allows it to cut sheet metal of varying thicknesses. Widely used in the production of metal covers or housings, gears, brackets, panels, signs, chassis, and precision laser cut parts.
Stainless steel (SUS304, SUS301, SUS430) can be precisely cut with metal cutting technology, with no slag on the edge, which can save labor costs for deburring. It is widely used in aerospace, automotive, shipbuilding, construction, medical, label/signage, electronics and electrical appliances.
Aluminum: Laser cutting aluminum requires precise and powerful technology, involving laser parameter adjustment, focus optimization, selection of appropriate nozzles and lenses, path compensation, etc. Aluminum sheet metal parts are widely used in transportation, automobiles, high-speed railways, aircraft and bridges, construction materials, electronics and electrical appliances, packaging and other industries due to their lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance and easy forming processing.
Copper: Laser cutting copper is efficient and accurate. Its high-intensity focused beam can penetrate copper materials to achieve clean and narrow incisions, which is especially suitable for fine and complex designs. Compared with traditional methods, laser cutting is more efficient and economical, especially for conductive materials such as copper. It is widely used in jewelry, electricity, construction, automobiles, chemicals and daily life.
Brass is a zinc-copper alloy, and fine adjustment of power and speed is required during laser cutting. High-intensity short-wavelength lasers are efficient and precise, and are particularly suitable for complex designs. Laser systems have high production capacity and low waste, and air assists clean cutting. Laser cut parts are widely used in architectural decoration, musical instrument production, electronics industry, transportation, construction and infrastructure, and daily necessities. It is also often used to make valves, water pipes, radiators, etc.
Laser cutting of titanium metal, due to its low density, strong gloss, and corrosion resistance, can form a dark and consistent etching effect on the metal surface using marking spray or oxygen auxiliary gas.
Occasional disadvantages of laser cutting of titanium and titanium alloys in metal plates: oxide layer and deformation. High heat can easily cause oxide layer, affecting the material and surface quality and reducing performance. Deformation is also common and can be easily caused by improper operation. It is recommended to use air as the auxiliary gas to avoid overburning and oxide layer problems caused by oxygen.
Titanium and titanium alloys are widely used in aviation, aerospace, ships, medical, chemical and other fields. In aviation, it is used for aircraft structural parts and engine parts; in aerospace, it is used for aerospace equipment, satellites, rockets; in ships, it is used for nuclear submarines, submersibles, etc.; in the medical field, it is used for orthopedic implants and dentures; in the chemical field, it is used for distillation towers, reactors, etc.; it is also used in transportation and automobile manufacturing. Laser cutting technology is also applicable to non-metals and other materials, such as plastics, wood, paper, etc.
How to choose a high-quality laser cutting processing service manufacturer?
Highly recommended—Futai manufacturer, specializing in sheet metal processing laser cutting services and production solutions. Whether it is complex laser cutting parts or small or large batch production, they can meet the personalized customization and fast on-demand manufacturing needs of global customers.



Conclusion
Sheet metal laser cutting technology is precise and efficient, making it an ideal choice for manufacturing complex parts.
Please feel free to contact us, our professional team will be happy to meet your laser cutting needs.
